- Trees and Their Essential Role in Biodiverse Ecosystems
- The Importance of Trees in Ecosystems
- Trees and Climate Regulation
- Trees as Habitat for Wildlife
- Trees and Soil Conservation
- Trees and Water Cycle
- Trees and Air Quality
- Trees and Carbon Sequestration
- Trees and Human Health Benefits
- Trees and Economic Value
- Trees and Cultural Significance
- Threats to Trees and Ecosystems
- Conservation and Restoration of Trees and Ecosystems
- FAQ:
- Why are trees important for biodiversity?
- How do trees contribute to the health of ecosystems?
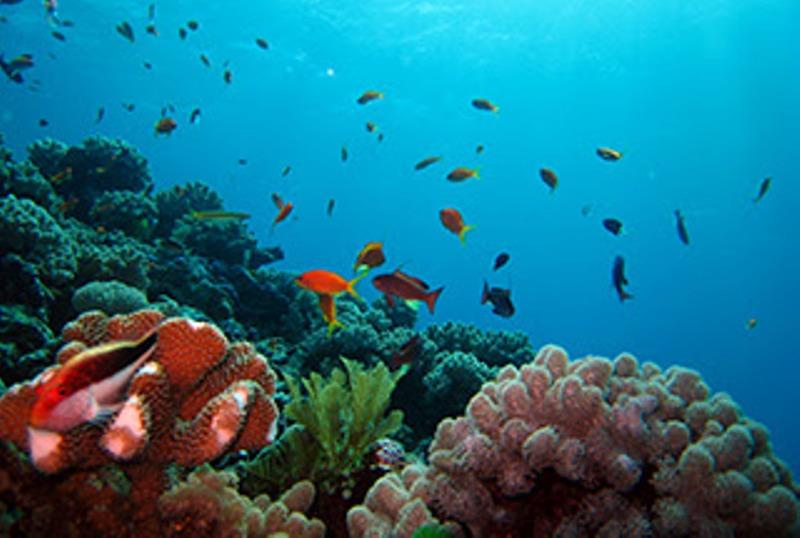
Trees and Their Essential Role in Biodiverse Ecosystems
Trees play an essential role in the health and sustainability of ecosystems around the world. They are not just a beautiful part of the landscape, but rather, they are the cornerstone of biodiverse ecosystems.
One of the key reasons why trees are so important is their ability to provide habitat and food for a wide variety of species. The branches and leaves of trees offer shelter and nesting sites for birds, while the fruits, nuts, and seeds they produce serve as a valuable food source for many animals.
In addition to supporting wildlife, trees also have a significant impact on the environment. They act as natural filters, absorbing harmful pollutants from the air and water. Through the process of photosynthesis, trees also release oxygen into the atmosphere, helping to combat climate change and improve air quality.
Furthermore, trees play a crucial role in maintaining soil health. Their roots help to stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and promoting water infiltration. The fallen leaves and branches of trees act as a natural mulch, enriching the soil with organic matter and providing nutrients for other plants to grow.
In conclusion, trees are not just a beautiful part of our natural landscapes, but they are also essential for the health and sustainability of ecosystems. They provide habitat and food for a wide variety of species, filter pollutants from the air and water, release oxygen, and promote soil health. It is crucial that we recognize the importance of trees and take steps to protect and conserve them for future generations.
The Importance of Trees in Ecosystems
Trees play an essential role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems. They are not only a source of oxygen, but they also provide habitat, food, and shelter for a wide variety of organisms. Without trees, many species would struggle to survive, and entire ecosystems would be disrupted.
One of the key roles that trees play in ecosystems is their ability to produce oxygen through photosynthesis. This process involves the conversion of carbon dioxide into oxygen, which is vital for the survival of all living organisms. In addition to producing oxygen, trees also absorb harmful greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate climate change.
Trees are also important for providing habitat for a diverse range of species. The branches and leaves of trees provide shelter and nesting sites for birds, squirrels, and other animals. Many insects also rely on trees for food and shelter, creating a complex web of interactions within the ecosystem.
Furthermore, trees contribute to the health of ecosystems by preventing soil erosion. Their roots help to stabilize the soil, preventing it from being washed away by rainwater or blown away by wind. This is particularly important in areas prone to flooding or strong winds, as trees can act as a natural barrier against these natural hazards.
In conclusion, trees are essential for the functioning of ecosystems. They provide oxygen, habitat, and food for a wide variety of organisms, and help to maintain the balance and health of the environment. Without trees, ecosystems would be severely disrupted, leading to a loss of biodiversity and the potential collapse of entire ecosystems.
Trees and Climate Regulation
Trees play an essential role in climate regulation, making them a vital component of biodiverse ecosystems. They act as natural air filters, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. This process helps to mitigate the impacts of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and stabilizing the Earth’s temperature.
Furthermore, trees also help to regulate local climate conditions. Their canopies provide shade, which helps to cool the surrounding area and reduce the need for artificial cooling systems. This is particularly important in urban environments, where the heat island effect can lead to higher temperatures. By planting more trees in cities, we can create a more comfortable and sustainable living environment.
In addition to their role in climate regulation, trees also play a crucial role in water management. Their roots help to stabilize soil, preventing erosion and reducing the risk of landslides. This is especially important in areas prone to heavy rainfall or flooding. Trees also act as natural water filters, absorbing excess nutrients and pollutants from the soil and preventing them from entering water bodies.
Overall, trees are an integral part of biodiverse ecosystems and have a significant impact on climate regulation. By preserving and planting more trees, we can help mitigate the effects of climate change, create healthier and more sustainable environments, and protect the biodiversity of our planet.
Trees as Habitat for Wildlife
Trees play a crucial role in providing habitat for a wide range of wildlife species. They are not only essential for the survival of many animals, but they also contribute to the overall health and balance of ecosystems.
One of the main reasons why trees are so important for wildlife is because they provide shelter and protection. The branches and leaves of trees create a safe haven for birds, squirrels, and other small animals to build their nests and raise their young. The dense foliage also offers protection from predators, such as hawks and owls.
In addition to providing shelter, trees also offer a valuable source of food for many animals. The fruits, nuts, and seeds produced by trees are a vital part of the diet for a variety of wildlife species. Birds, squirrels, and other small mammals rely on these food sources to survive, especially during the winter months when other food options are scarce.
Furthermore, trees support a diverse range of insects, which in turn serve as a food source for larger animals. Insects such as bees, butterflies, and beetles are attracted to the flowers and leaves of trees, providing a crucial source of food for birds and other insect-eating animals. This interconnected web of life demonstrates the essential role that trees play in supporting biodiverse ecosystems.
In conclusion, trees are not just beautiful and majestic organisms; they are also vital for the survival and well-being of wildlife. From providing shelter and protection to offering a source of food, trees are the cornerstone of biodiverse ecosystems, ensuring the continued existence of a wide range of animal species. It is crucial that we recognize the importance of trees and take steps to protect and preserve them for future generations.
Trees and Soil Conservation
Trees play a crucial role in soil conservation within biodiverse ecosystems. Their presence is essential for maintaining the health and fertility of the soil.
One way trees contribute to soil conservation is through their extensive root systems. The roots of trees help to stabilize the soil, preventing erosion caused by wind and water. They act as anchors, holding the soil in place and reducing the risk of landslides and mudslides.
Furthermore, trees also contribute to soil conservation through the process of leaf litter decomposition. When leaves fall from the trees, they create a layer of organic matter on the forest floor. This layer acts as a natural mulch, protecting the soil from the impact of raindrops and reducing water runoff. The decomposition of the leaf litter also adds nutrients to the soil, enhancing its fertility and supporting the growth of other plants.
In addition to their root systems and leaf litter, trees also play a role in soil conservation through their ability to absorb and retain water. When it rains, trees capture and store water in their roots, trunk, and branches. This not only helps to prevent soil erosion by reducing the force of raindrops on the soil surface, but it also helps to recharge groundwater reserves and maintain the moisture levels in the soil.
In conclusion, trees are essential for soil conservation in biodiverse ecosystems. Their roots stabilize the soil, their leaf litter protects it from erosion, and their ability to absorb and retain water helps to maintain its moisture levels. Without trees, the soil would be more vulnerable to erosion, leading to the degradation of the entire ecosystem.
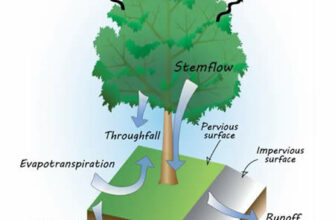
Trees and Water Cycle
Trees play a crucial role in the water cycle, which is essential for the survival of ecosystems. Through a process called transpiration, trees release water vapor into the atmosphere, contributing to the formation of clouds and precipitation.
Transpiration occurs when trees absorb water from the soil through their roots and release it into the air through small pores on their leaves, called stomata. This process not only helps to regulate the temperature of the trees but also helps to distribute water across the landscape.
The water released by trees through transpiration is important for the replenishment of groundwater and the maintenance of river flows. It also helps to prevent soil erosion by keeping the ground moist and stable. Without trees, the water cycle would be disrupted, leading to a decrease in rainfall and the loss of essential water resources.
In addition to their role in transpiration, trees also act as natural water filters. As water moves through the soil, tree roots absorb and filter out pollutants, such as excess nutrients and chemicals. This helps to improve water quality and protect aquatic ecosystems.
Overall, trees are fundamental to the water cycle and the health of ecosystems. They not only contribute to the distribution of water and the prevention of erosion but also help to maintain water quality and support diverse plant and animal life. Therefore, it is crucial to protect and conserve trees to ensure the sustainability of our natural water resources.
Trees and Air Quality
Trees play a crucial role in maintaining the air quality in ecosystems. They are essential for filtering and purifying the air we breathe.
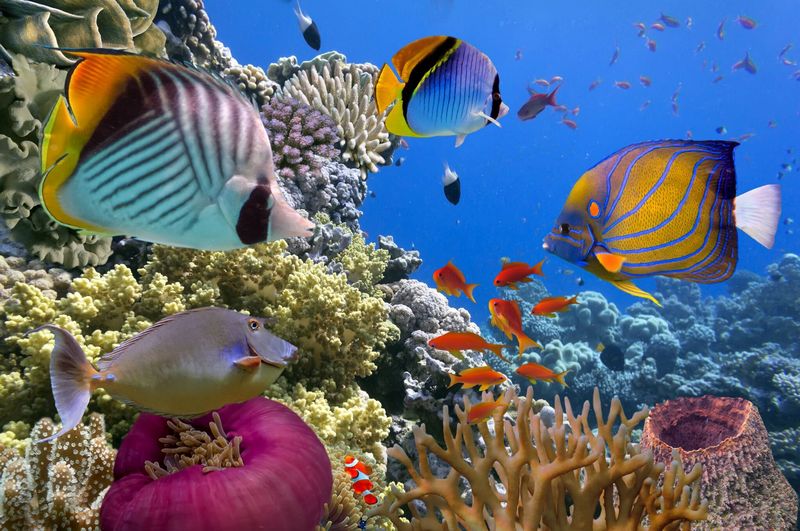

One of the main ways trees contribute to air quality is through the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to reduce the levels of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. In addition, trees also trap and store carbon, which helps to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, trees act as natural air filters by capturing and removing pollutants from the air. Their leaves, bark, and roots can absorb and break down harmful chemicals and pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter. This not only improves air quality but also reduces the risk of respiratory diseases and other health issues caused by air pollution.
Another way trees contribute to air quality is by providing shade. By shading buildings and urban areas, trees can help to reduce the need for air conditioning, which in turn reduces energy consumption and the emissions of greenhouse gases from power plants.
In conclusion, trees play a vital role in maintaining air quality in ecosystems. Through photosynthesis, they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to reduce greenhouse gas levels. Trees also act as natural air filters, capturing and removing pollutants from the air. Their shade can also help to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, preserving and planting trees is crucial for ensuring clean and healthy air for both humans and wildlife.
Trees and Carbon Sequestration
Trees play a crucial role in the carbon sequestration process, which is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems and mitigating climate change. Through the process of photosynthesis, trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their trunks, branches, and leaves. This process helps to remove greenhouse gases from the air, reducing the concentration of carbon dioxide, a major contributor to global warming.
Not only do trees sequester carbon, but they also release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. This oxygen is vital for the survival of many organisms, including humans. In addition, trees provide habitat for a diverse range of species, supporting biodiversity and promoting the overall health of ecosystems. They act as a natural filter, improving air and water quality, and reducing the impact of pollutants.
The role of trees in carbon sequestration is particularly important in biodiverse ecosystems, where the variety of plant and animal species is high. These ecosystems have a greater capacity to sequester carbon due to the abundance and diversity of trees. In tropical rainforests, for example, the dense vegetation and tall trees enable the storage of large amounts of carbon. Protecting and restoring these ecosystems is crucial for maintaining global carbon balance and preserving biodiversity.
In order to maximize the carbon sequestration potential of trees, it is important to prioritize the conservation and sustainable management of forests. This includes preventing deforestation, promoting reforestation and afforestation efforts, and implementing sustainable forestry practices. By recognizing the value of trees in carbon sequestration, we can work towards a more sustainable future and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Trees and Human Health Benefits
Trees play a crucial role in maintaining human health and well-being. They are not only aesthetically pleasing but also provide a wide range of benefits that contribute to a healthier environment. One of the key benefits of trees is their ability to improve air quality. Through a process called photosynthesis, trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, which is essential for human survival. In addition, trees also filter out pollutants and particulate matter from the air, reducing the risk of respiratory diseases and improving overall air quality.
Furthermore, trees have a positive impact on mental health. Spending time in green spaces with trees has been shown to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. The presence of trees in urban areas has been linked to lower crime rates and increased community engagement. The shade provided by trees also helps to cool down urban environments, reducing the risk of heat-related illnesses during hot summer months.
In biodiverse ecosystems, trees play a critical role in supporting a wide variety of wildlife, including birds, insects, and mammals. This biodiversity has a direct impact on human health as well. By providing habitats for pollinators, trees contribute to the production of fruits, vegetables, and nuts, which are essential for a balanced and nutritious diet. Additionally, trees help to regulate water cycles, prevent soil erosion, and improve water quality, all of which are essential for human health and the sustainability of ecosystems.
In conclusion, trees are not just beautiful elements of nature, but they are also essential for human health and well-being. Their ability to improve air quality, promote mental well-being, support biodiversity, and regulate ecosystems makes them a vital component of our environment. It is crucial to recognize and protect the value of trees and ensure their preservation for the benefit of present and future generations.
Trees and Economic Value
Trees play an essential role in the economy, providing numerous economic benefits. One of the most significant ways trees contribute to the economy is through their provision of timber. The timber industry is a vital sector that relies heavily on trees for the production of wood products, such as furniture, construction materials, and paper.
Furthermore, trees can also have a positive impact on property values. Research has shown that homes surrounded by trees are often more desirable and can command higher prices in the real estate market. The shade and aesthetic value provided by trees can enhance the quality of life for residents and attract potential buyers.
In addition to their direct economic contributions, trees also play a crucial role in supporting biodiversity, which has indirect economic benefits. Biodiverse ecosystems are more resilient and can provide valuable ecosystem services, such as pollination, water filtration, and climate regulation. These services are essential for agriculture, tourism, and other industries, contributing to the overall economy.
Moreover, trees can also contribute to the economy through the provision of recreational opportunities. Forests and parks attract visitors who engage in activities such as hiking, camping, and wildlife watching. These activities can generate revenue for local communities through tourism and the sale of related goods and services.
Overall, trees have a significant economic value that extends beyond their direct contributions. They provide timber, enhance property values, support biodiversity, and offer recreational opportunities. Recognizing the economic importance of trees is crucial for sustainable development and the preservation of our natural resources.
Trees and Cultural Significance
Trees play an essential role in various cultural traditions and beliefs around the world. They hold significant cultural and spiritual value for many indigenous communities and are often considered sacred. These biodiverse giants are regarded as symbols of strength, wisdom, and longevity.
In many cultures, specific trees are associated with certain gods or deities and are worshipped as sacred beings. For example, the Bodhi tree in Buddhism is believed to be the tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment, making it a revered symbol for Buddhists. Similarly, the oak tree holds great importance in Celtic mythology and is associated with gods and goddesses of wisdom and fertility.
Trees are also deeply rooted in cultural practices and traditions. The practice of planting and caring for trees is a common ritual in many cultures, symbolizing the connection between humans and nature. In Japan, the art of bonsai, which involves carefully cultivating small trees in containers, is seen as a form of meditation and an expression of harmony with nature.
Furthermore, trees have inspired countless artistic expressions throughout history. From ancient cave paintings to famous works of literature and poetry, trees have been a subject of fascination and inspiration for artists across different cultures. They are often portrayed as a symbol of beauty, resilience, and the cycle of life.
Overall, trees hold immense cultural significance and are deeply intertwined with human beliefs, traditions, and artistic expressions. Their presence in our lives goes beyond their ecological importance, reminding us of our connection to the natural world and the need to protect and preserve these biodiverse ecosystems.
Threats to Trees and Ecosystems
Trees play an essential role in maintaining biodiverse ecosystems. They provide habitat for numerous species, contribute to carbon sequestration, and help regulate local climate. However, trees and the ecosystems they support face various threats that can have significant impacts on their survival and biodiversity.
One major threat to trees and ecosystems is deforestation. This practice involves the clearing of large areas of forest for agriculture, logging, or urban development. Deforestation not only destroys trees but also disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to the loss of habitat for countless species and the disruption of ecological processes.
Another threat to trees and ecosystems is invasive species. These non-native plants and animals can outcompete native species for resources, disrupt food chains, and alter the structure and function of ecosystems. Invasive species can harm trees directly by feeding on them or indirectly by affecting their pollinators or seed dispersers.
Climate change is also a significant threat to trees and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can negatively impact tree growth, reproduction, and survival. Climate change can also alter the distribution of species, leading to shifts in ecosystem composition and dynamics.
Pollution is yet another threat to trees and ecosystems. Air and water pollution can harm trees directly by damaging their leaves, roots, and bark. It can also indirectly affect trees by altering soil composition and nutrient availability. Pollution can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems and contribute to the decline of both tree and animal species.
To address these threats and protect trees and ecosystems, it is crucial to implement sustainable land management practices, promote reforestation and habitat restoration, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Conservation efforts should focus on preserving and restoring native tree species and promoting biodiversity in ecosystems. By safeguarding trees and ecosystems, we can ensure the continued provision of essential ecosystem services and maintain the health and resilience of our planet.
Conservation and Restoration of Trees and Ecosystems
Conservation and restoration efforts for trees and ecosystems are essential for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the health and stability of our natural environment. Trees play a crucial role in supporting diverse ecosystems by providing habitat for numerous species, regulating temperature and climate, and filtering air and water.
Conservation efforts focus on protecting existing trees and preventing their destruction through practices such as sustainable logging, land-use planning, and protected area designation. These measures help to preserve the biodiversity and ecological functions that trees provide, ensuring the long-term health of ecosystems.
Restoration initiatives aim to reverse the damage caused by deforestation and other forms of habitat destruction. This involves planting new trees in areas that have been cleared or degraded, as well as rehabilitating degraded ecosystems to promote their recovery. Restoring trees and ecosystems not only helps to mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide, but also enhances biodiversity and improves the resilience of ecosystems to future disturbances.
Conservation and restoration efforts often involve collaboration between governments, non-governmental organizations, local communities, and other stakeholders. These initiatives may include education and awareness campaigns, policy development, and the implementation of sustainable land management practices. By working together, we can protect and restore trees and ecosystems, ensuring the continued provision of essential ecosystem services and the preservation of biodiversity for future generations.
FAQ:
Why are trees important for biodiversity?
Trees are important for biodiversity because they provide habitat for a wide variety of species. Their branches and trunks create homes for birds, squirrels, insects, and other animals. Additionally, trees provide food and shelter for many organisms, and their leaves and fruits are an important food source for herbivores. Without trees, many species would lose their homes and sources of food, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
How do trees contribute to the health of ecosystems?
Trees contribute to the health of ecosystems in several ways. Firstly, they help to regulate the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. This helps to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigate climate change. Secondly, trees help to prevent soil erosion by anchoring the soil with their roots. This is especially important in areas with steep slopes or prone to heavy rainfall. Lastly, trees provide shade and reduce the temperature in their surroundings, creating a more favorable environment for other plants and animals.